Research on Safety Characteristic of Mobile Gas Cooled Reactor System
-
摘要:
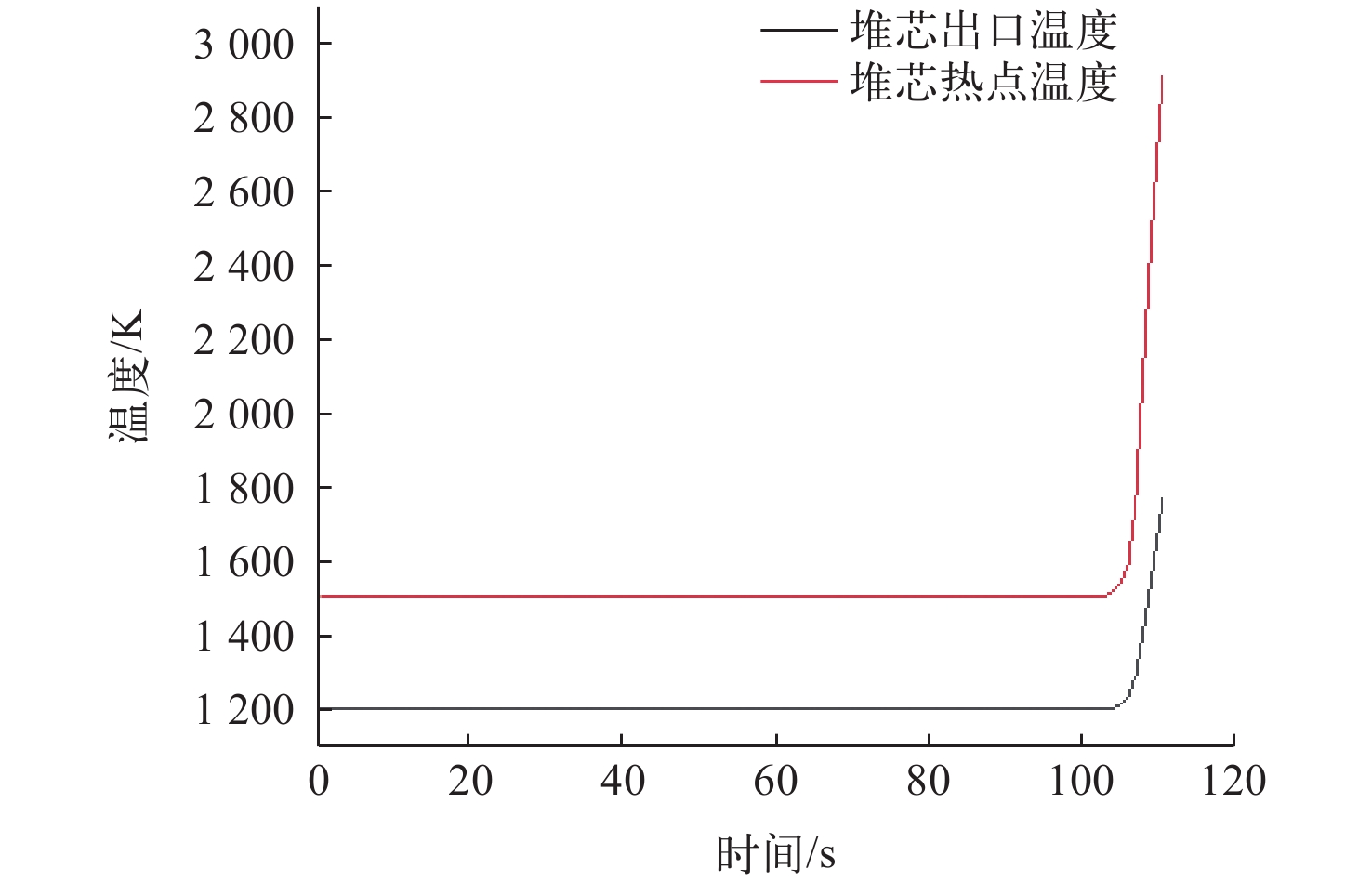
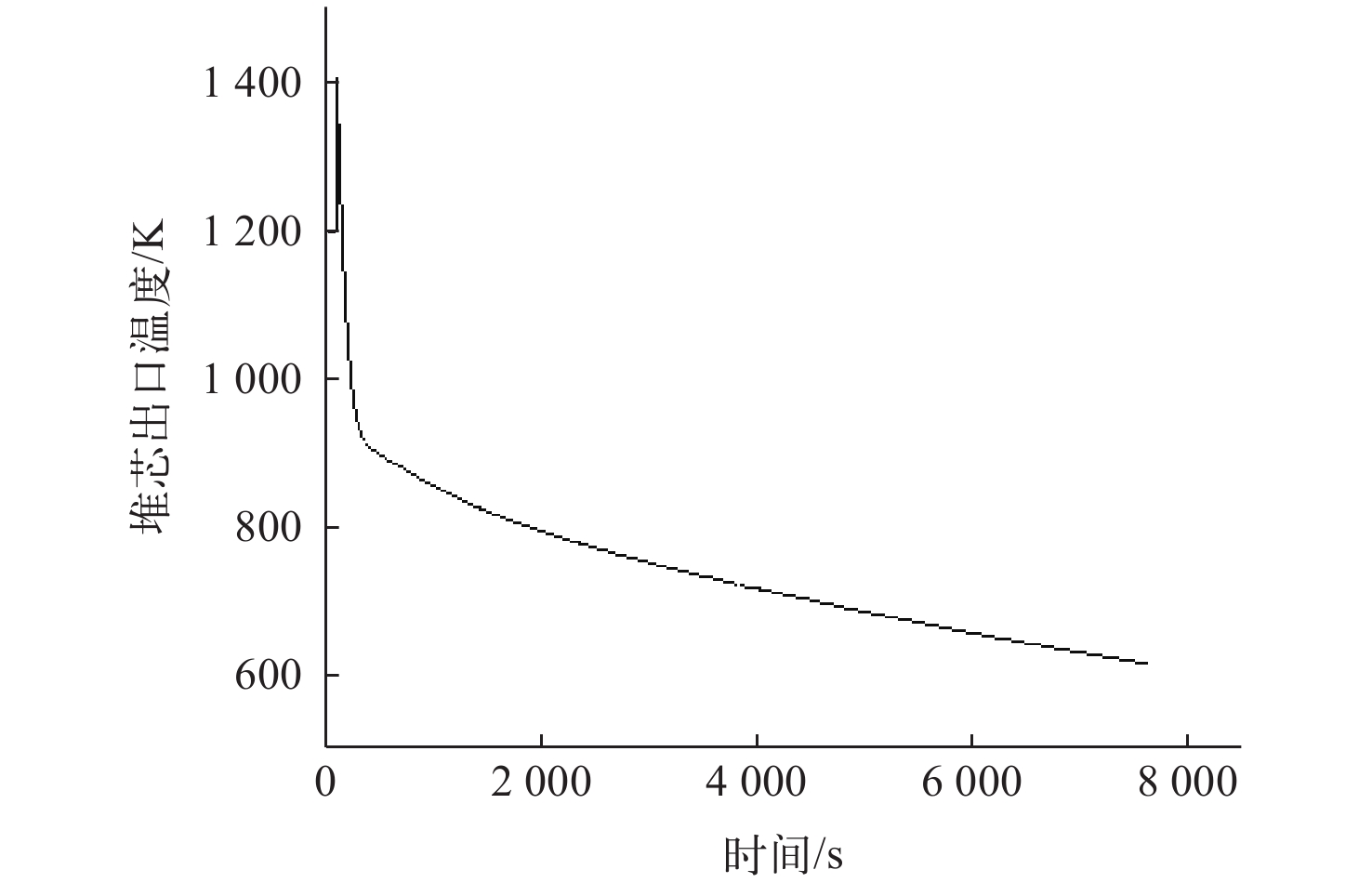
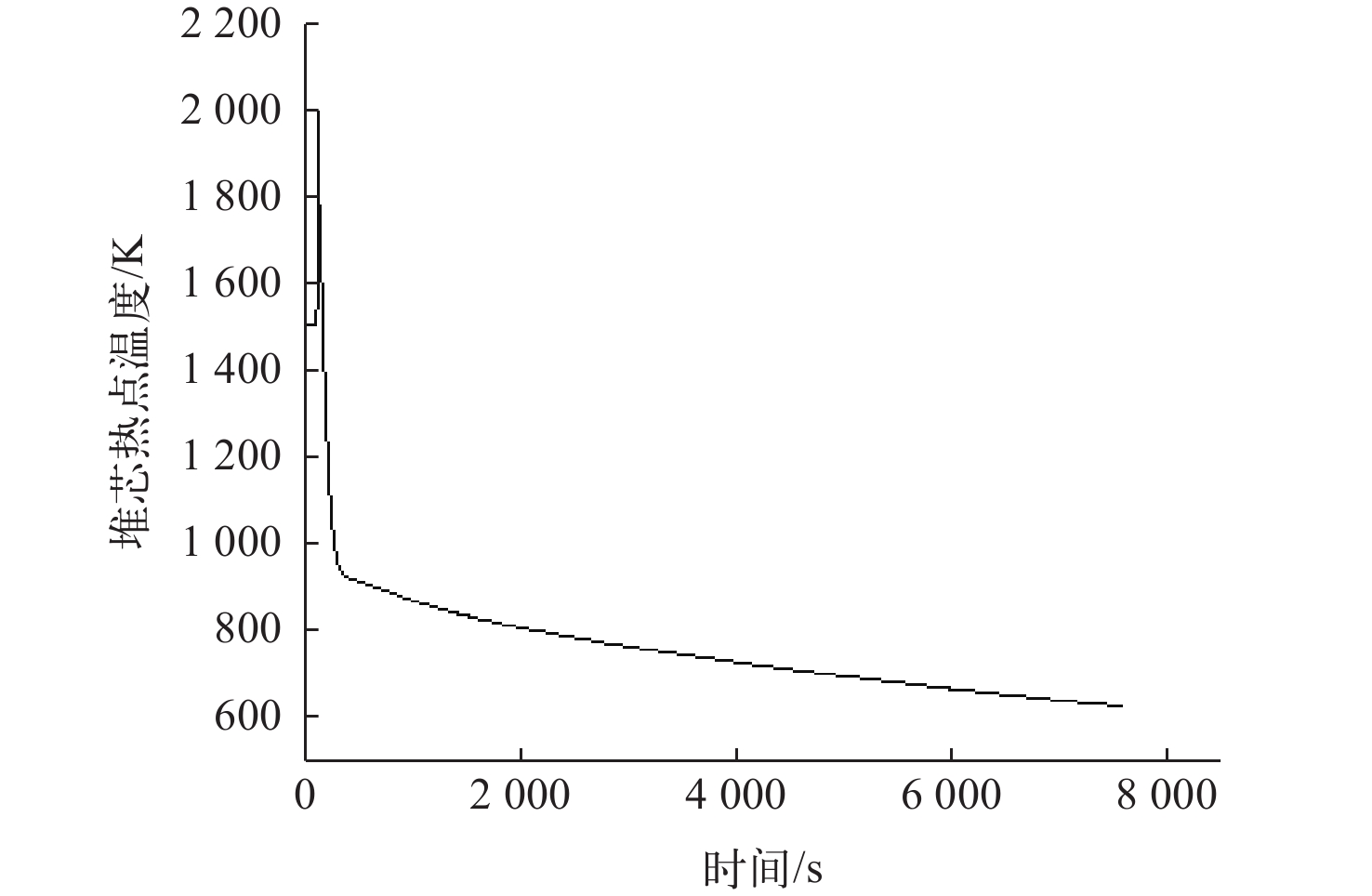
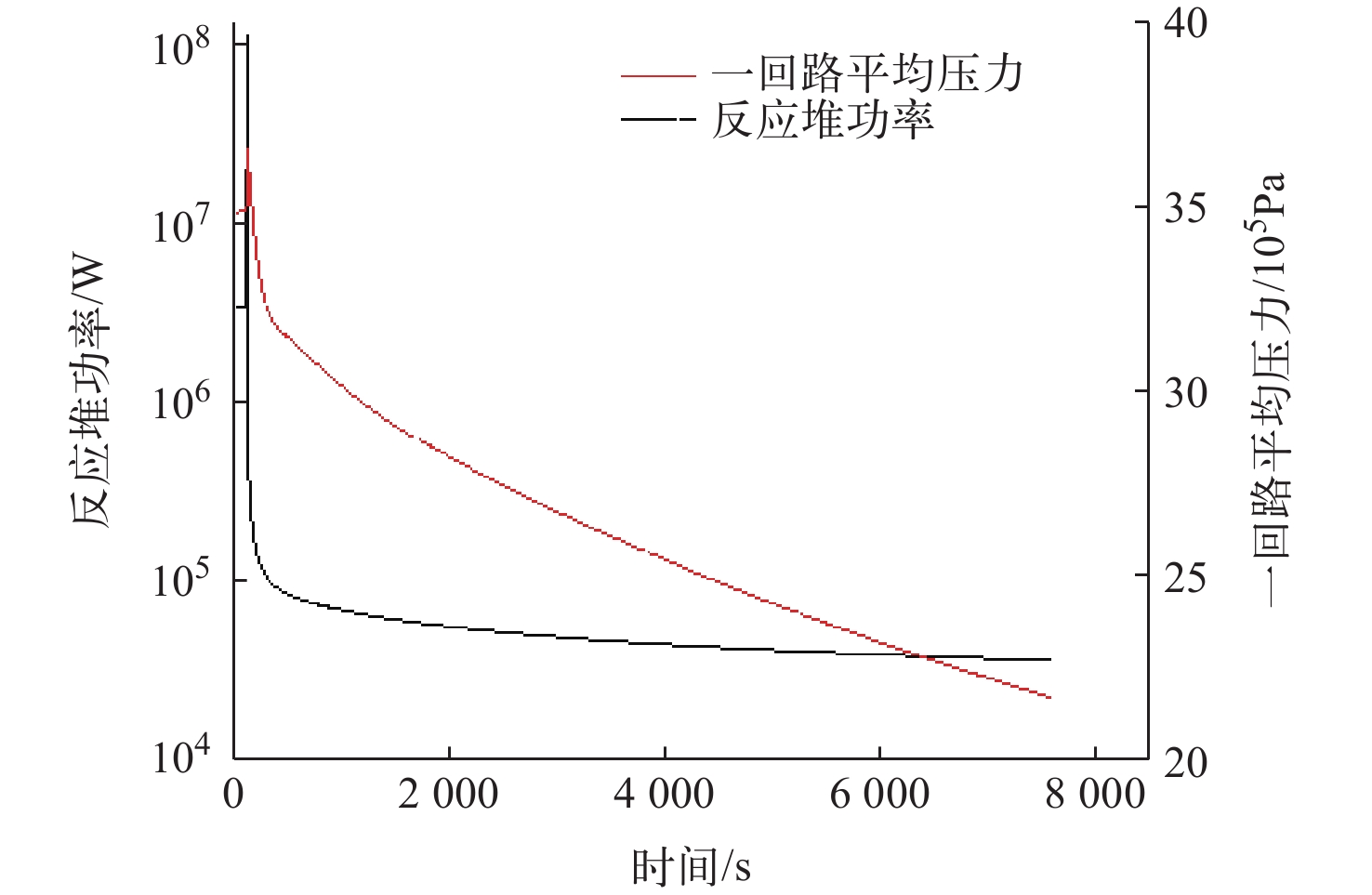
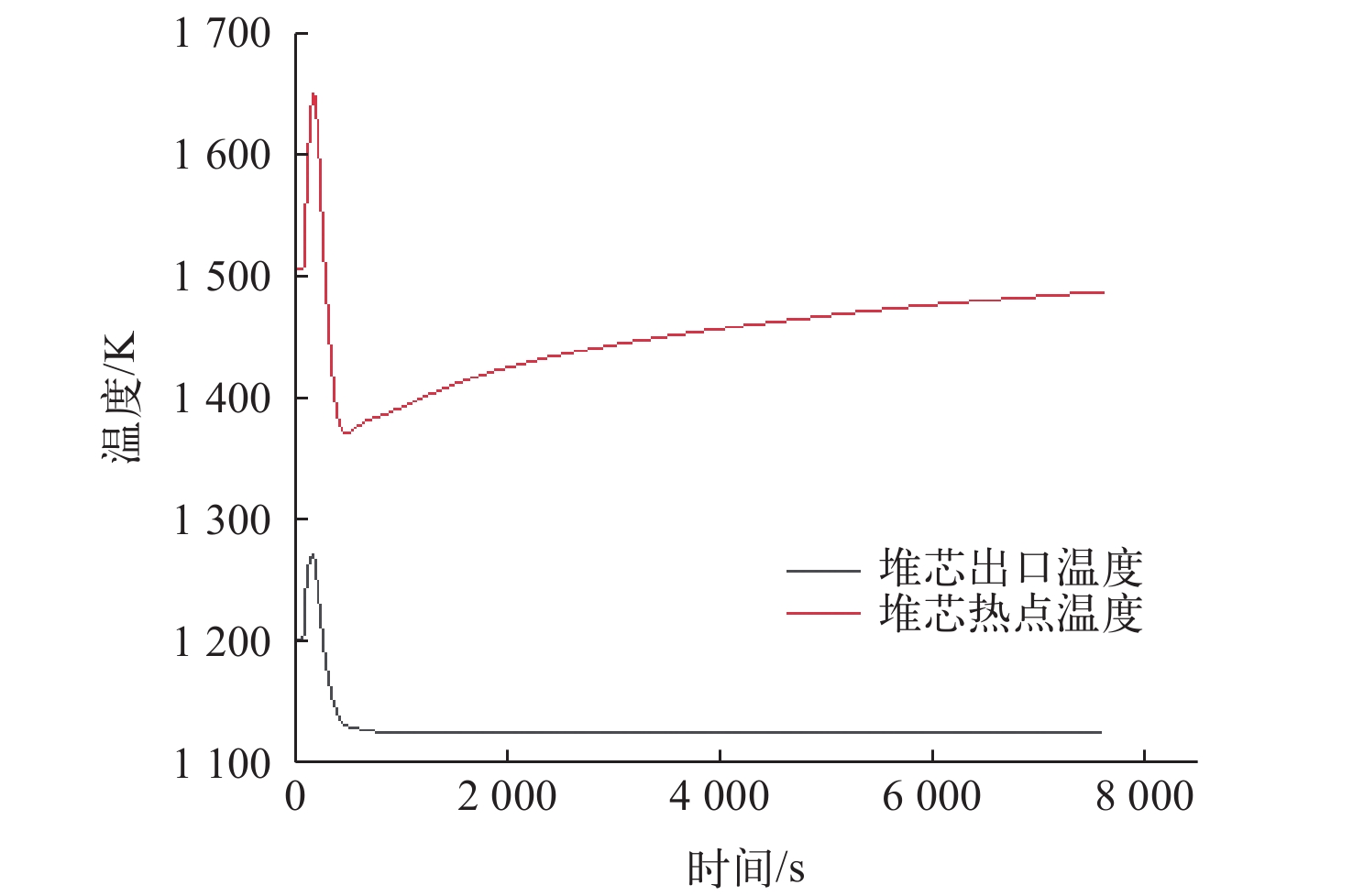
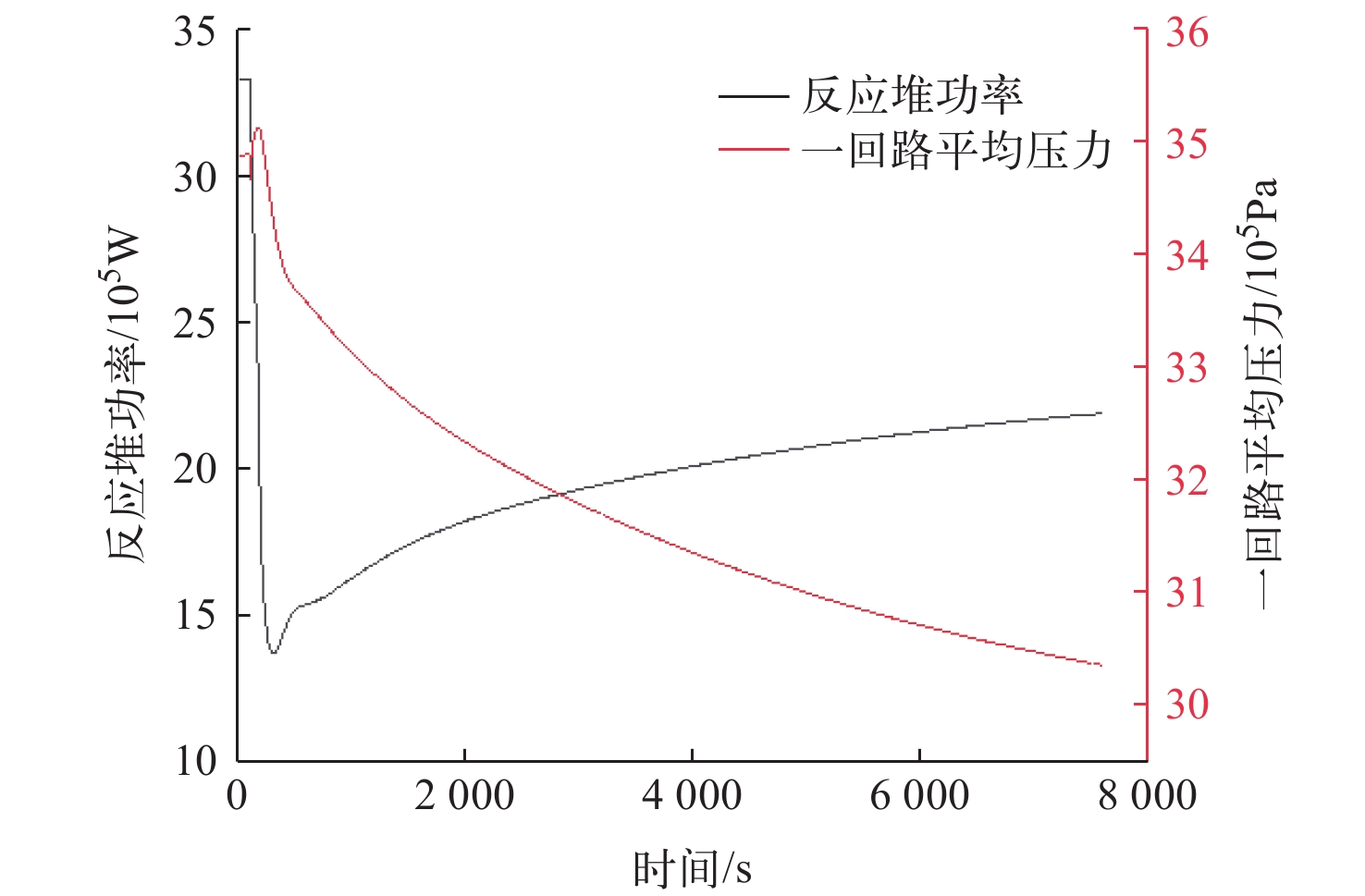
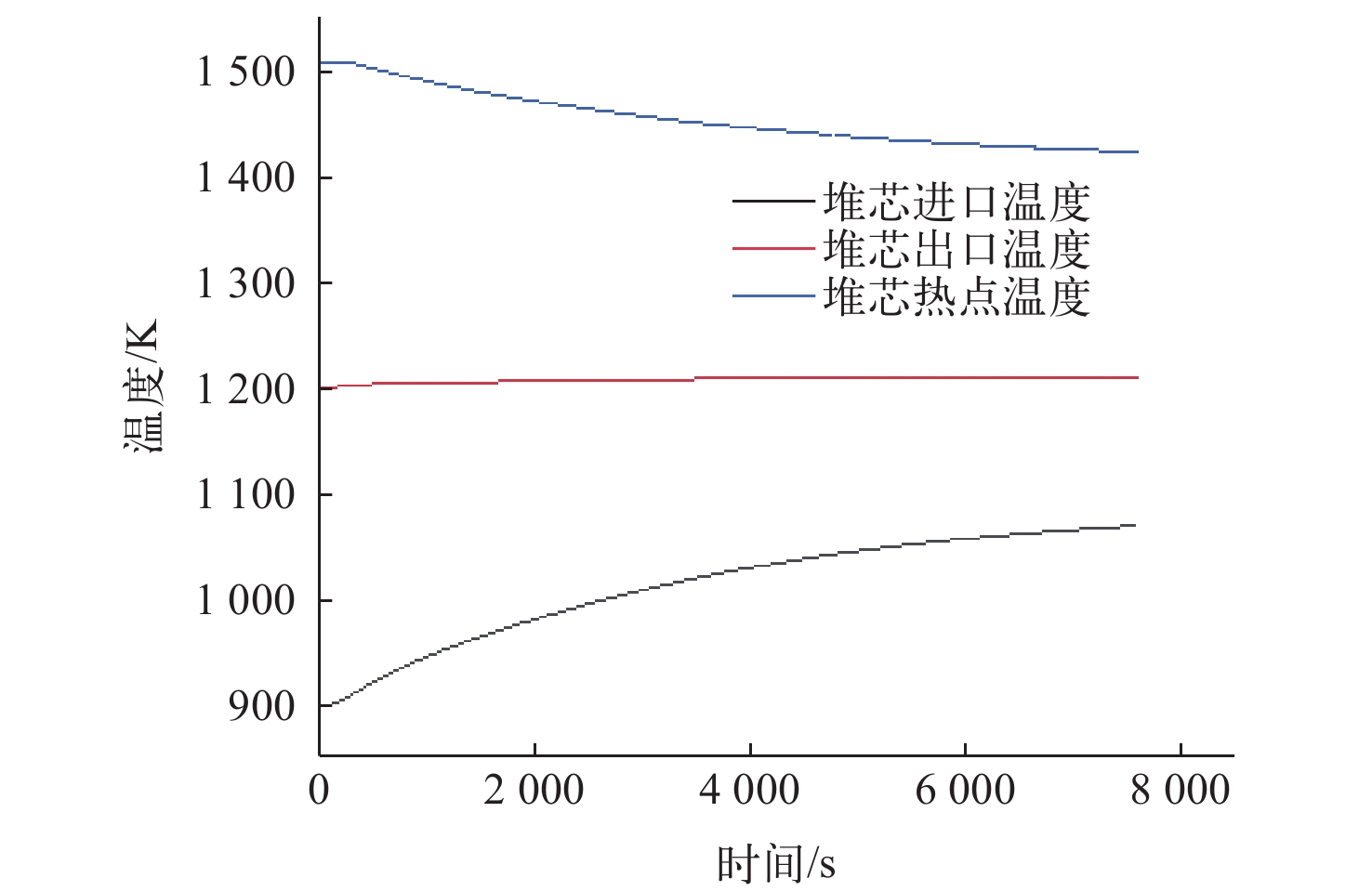
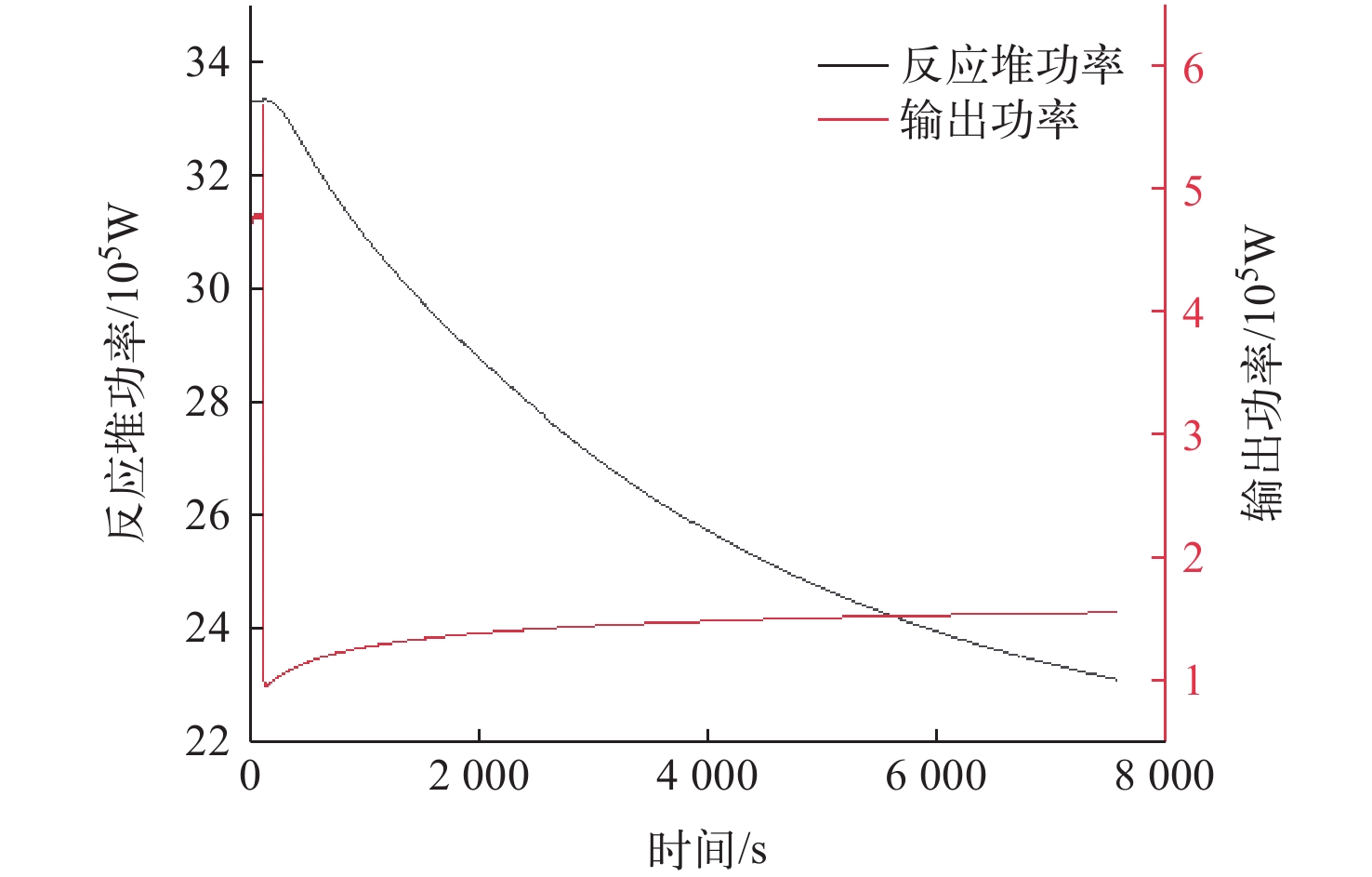
为了对布雷顿氦氙气冷堆系统的稳态和事故工况进行研究,本文依据系统设计参数,使用RELAP5/MOD程序对系统进行建模与仿真计算。对系统的稳态工况进行了计算,结果与设计值的最大相对偏差为3.08%,验证了模型的准确性,为后续系统优化打下基础。对反应堆系统可能发生的3种事故工况进行了研究分析,分别为控制系统故障、一回路风机故障和涡轮机故障。对3种事故中堆芯冷却剂出口温度、堆芯热点温度、反应堆功率等关键参数进行计算,并研究了事故发生后各关键参数的变化趋势,对反应堆系统的安全特性进行了分析和验证。结果表明,本文所建立的模型可较准确地对布雷顿氦氙气冷堆系统的各工况进行仿真,在保护系统生效时反应堆系统是安全的。对于控制系统故障导致以0.001 s−1增加了0.02的反应性的反应性引入事故,当保护系统失效时,在事故发生9 s后,堆芯热点温度为2 493.061 K,堆芯将会损毁;当保护系统正常时,系统将在保护系统的作用下安全停堆。对于一回路风机故障导致一回路流量下降至50%和涡轮机故障导致其中一条二回路流量下降至60%的事故,反应堆系统均可保持安全状态。
-
关键词:
- RELAP5/MOD程序 ,
- 布雷顿循环 ,
- 氦氙气冷堆 ,
- 安全特性
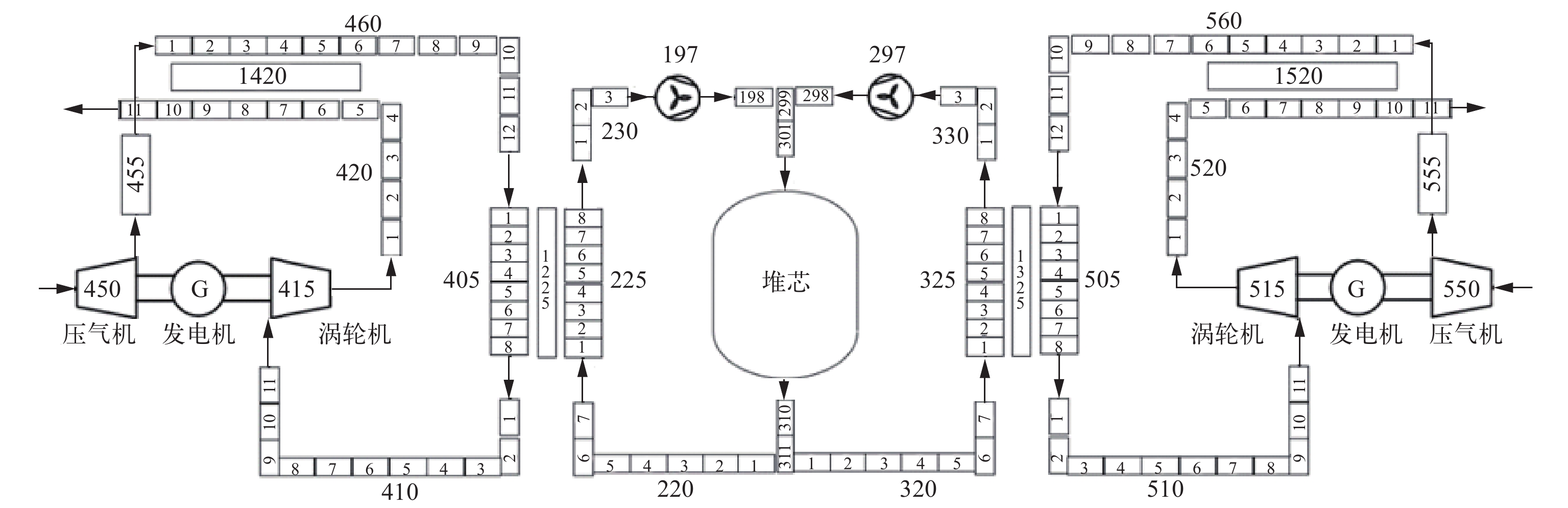
Abstract:Small mobile reactors have the characteristic of being able to adapt to the multielement energy needs of different geographical environments and application scenarios, and are currently one of the important candidate solutions for solving diversified power demands in civilian field. Then the Brayton cycle is a commonly used form of thermoelectric conversion device for reactor power due to its advantages of fast start-up, simple system, high economic efficiency, and high efficiency. The gas cooled reactor coupled with Brayton cycle is a widely studied field by scholars both domestically and internationally. In order to investigate the key safety features of He-Xe gas cooled reactor systems coupled with Brayton cycle, this paper used RELAP5/MOD code to model the system based on its design parameters, and simulated and analyzed the system’s stability and potential accident conditions. The model established in this paper was composed of a He-Xe gas cooled reactor coupled with two sets of open Brayton power generation modules, where the He-Xe gas cooled reactor was the primary loop and the working fluid was He-Xe gas at 40 g/mol. The Brayton cycle was the secondary loop with air as the working fluid. The steady-state condition of the system was simulated, and the simulation parameters were compared with the original design values. The results show that maximum relative error is 3.08%, which proves the accuracy of the model. For the reactivity insertion accident caused by a control system failure resulting in an increase of 0.02 reactivity at a rate of 0.001 s−1, when the reactor protection system fails, the reactor core hotspot temperature will reach 2 493.061 K 9 seconds after the accident, which exceeds the safe temperature of the system and will cause breakdown. When the reactor protection system is effective, the reactor shutdown protection will be triggered 11 seconds after the accident, and the reactor core temperature will be 2 001.581 K, then the reactor can shut down safely. For the loss of flow accident caused by a failure of the primary loop fan, the reactor core hotspot temperature will be 1 650.851 K, and the reactor will continue to operate in a new steady state thereafter. For the one of the secondary turbine faults caused a 40% decrease in mass flow rate in the loop, the reactor core hotspot temperature will be 1 507.644 K. After the system stabilizes, the reactor continue to operate at 33% rated power. The results indicate that the model established in the paper can accurately simulate various operating conditions of the Brayton He-Xe gas cooled reactor system, and the system is safe in the event of the three accidents mentioned above when the protection system is effective.
-
Keywords:
- RELAP5/MOD code ,
- Brayton cycle ,
- He-Xe gas cooled reactor ,
- safety feature
-
-
表 1 堆芯设计参数
Table 1 Reactor core design parameter
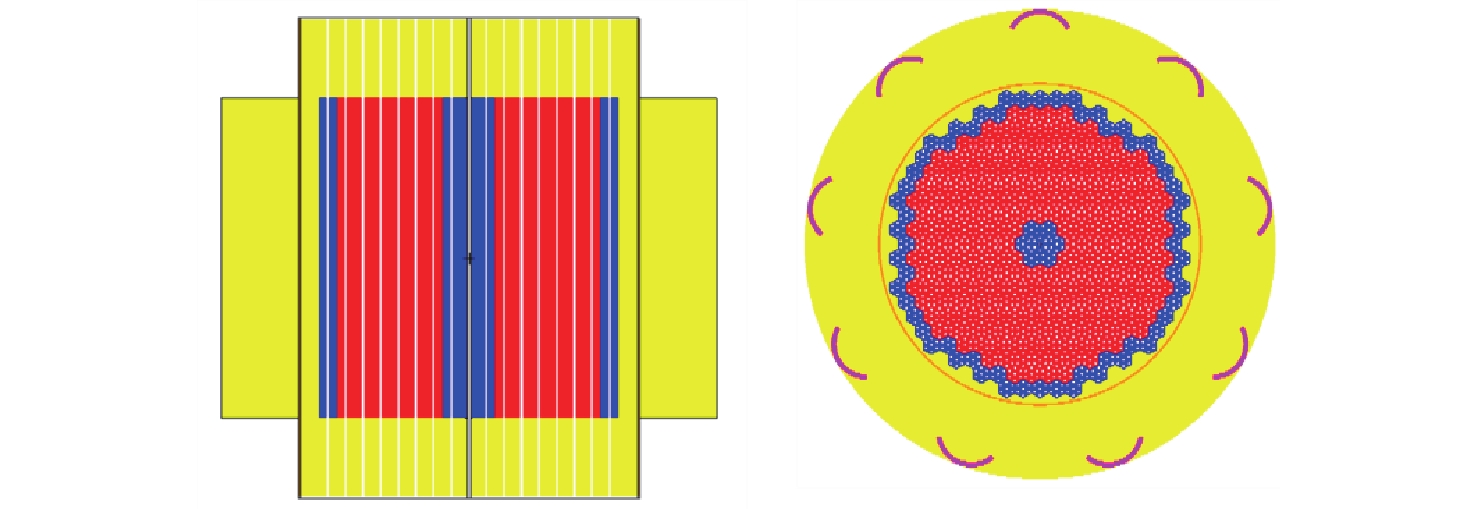
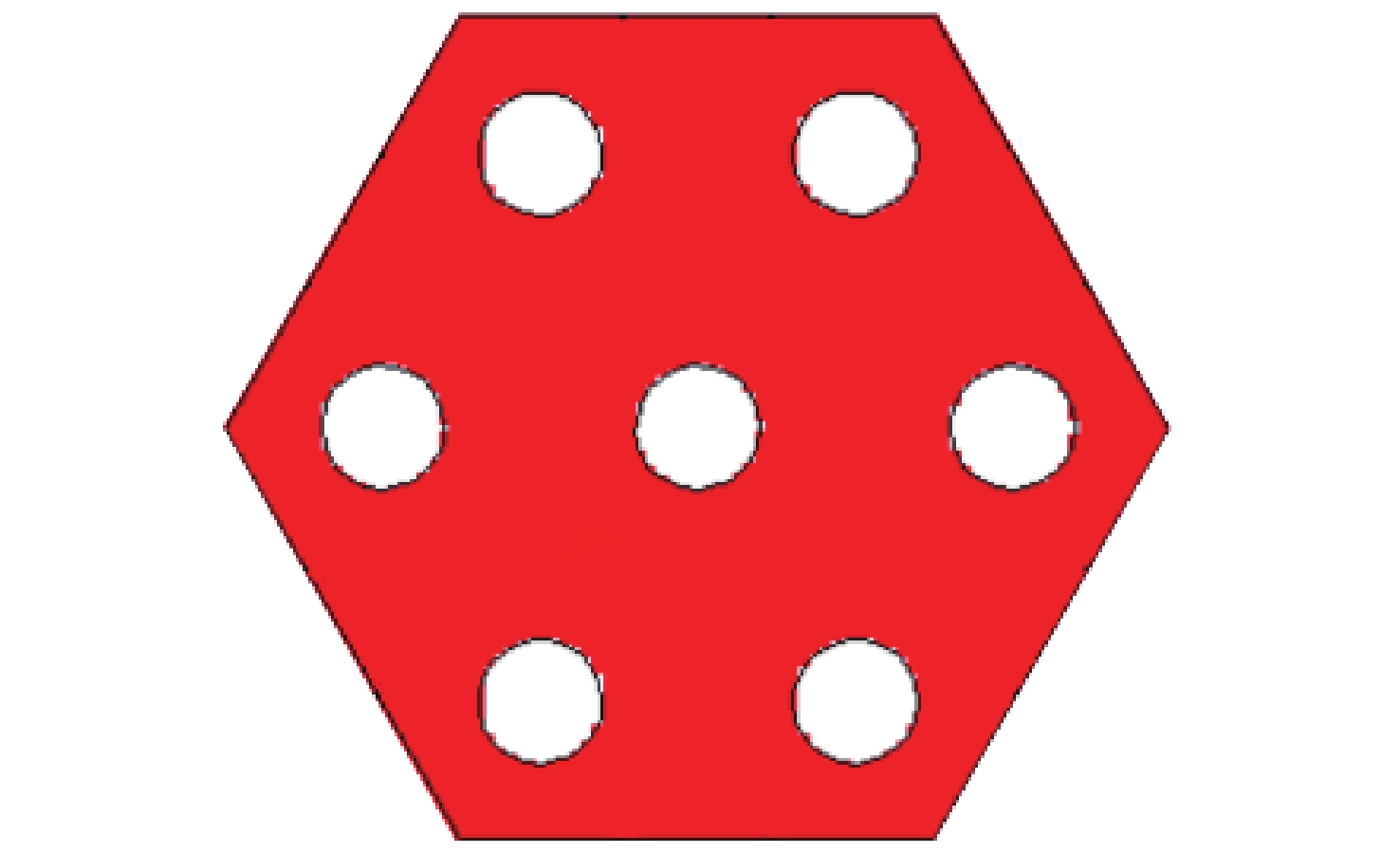
参数 参数值 堆芯高度,cm 90 堆芯直径,cm 94 活性区直径,cm 63 活性区高度,cm 60 堆芯容器材料 不锈钢 反射层材料 BeO 径向反射层内径,cm 64 径向反射层厚度,cm 15 径向反射层高度,cm 60 端部反射层厚度,cm 15 控制鼓个数 9 控制鼓吸收体材料 B4C(90%10B) 控制鼓吸收体厚度,cm 1.0 燃料元件数目 295 燃料元件材料 TRISO球-石墨基体 燃料元件长度,cm 15 冷却剂孔道数量 7 冷却剂孔道间距,cm 1.27 冷却剂孔道直径,mm 4.5 表 2 系统稳态模拟结果
Table 2 System steady-state simulation result
参数 参数值 相对误差/% 设计值 模拟值 反应堆入口温度,K 887 895.511 0.96 反应堆出口温度,K 1 200 1 201.601 0.13 反应堆额定热功率,MW 3.329 3.233 2.88 涡轮机1入口温度,K 1 123 1 122.125 0.08 涡轮机1出口温度,K 899 912.931 1.55 涡轮机1入口压力,kPa 296.94 302.835 1.99 涡轮机1出口压力,kPa 136.32 132.388 2.88 涡轮机2入口温度,K 1 123 1 121.599 0.12 涡轮机2出口温度,K 899 912.812 1.54 涡轮机2入口压力,kPa 296.94 302.826 1.98 涡轮机2出口压力,kPa 136.32 132.557 2.76 压气机1压比 3 3.044 1.47 压气机1出口温度,K 440 435.599 1.00 压气机2压比 3 3.044 1.47 压气机2出口温度,K 440 435.586 1.00 系统效率,% 30.19 31.12 3.08 -
[1] 邱建文, 徐瑞, 赵宇庭. 小型核反应堆自主控制及其深空探测应用设想[J]. 宇航学报, 2019, 40(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2019.01.001 QIU Jianwen, XU Rui, ZHAO Yuting. Autonomous control of small nuclear reactor and its applications for deep space exploration[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2019, 40(1): 1-8(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2019.01.001
[2] 郭佳欣, 陈晓亮. 小型移动式铅铋堆整堆运输临界安全问题研究[J]. 科技创新导报, 2022(12): 5-10. [3] 房勇汉, 刘达, 李林蔚, 等. 第四代核能系统发展现状分析与对策建议[J]. 产业与科技论坛, 2022, 21(23): 19-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5641.2022.23.007 FANG Yonghan, LIU Da, LI Linwei, et al. Analysis of the development status of the fourth generation nuclear energy system and countermeasures and suggestions[J]. Industrial & Science Tribune, 2022, 21(23): 19-20(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5641.2022.23.007
[4] ZHANG Z, YU S. Future HTGR developments in China after the criticality of the HTR-10[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2002, 218(1/2/3): 249-257.
[5] 李海鹏, 黄晓津, 张良驹. 10 MW高温气冷堆的集总参数动态模型[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2008, 42(5): 442-446. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2008.42.05.0442 LI Haipeng, HUANG Xiaojin, ZHANG Liangju. Lumped parameter dynamic model of 10 MW high-temperature gas-cooled reactor[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2008, 42(5): 442-446(in Chinese). doi: 10.7538/yzk.2008.42.05.0442
[6] 明杨, 易经纬, 方华伟, 等. 直接布雷顿循环气冷反应堆系统运行特性分析[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2020, 54(7): 1168-1175. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2020.youxian.0013 MING Yang, YI Jingwei, FANG Huawei, et al. Analysis of operating characteristic of direct Brayton cycle gas-cooled reactor system[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2020, 54(7): 1168-1175(in Chinese). doi: 10.7538/yzk.2020.youxian.0013
[7] 刘秀婷, 黄彦平, 汪杨乐, 等. 小型氟盐冷却高温堆耦合布雷顿循环系统分析与研究[J]. 核动力工程, 2022, 43(5): 20-26. LIU Xiuting, HUANG Yanping, WANG Yangle, et al. Analysis and research of coupled Brayton cycle system for small fluorine salt cooled high temperature reactor[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2022, 43(5): 20-26(in Chinese).
[8] 卢恒, 赵恒, 戴叶, 等. 熔盐堆超临界二氧化碳布雷顿循环系统与热力学分析[J]. 核动力工程, 2022, 43(2): 32-39. LU Heng, ZHAO Heng, DAI Ye, et al. MSR supercritical carbon dioxide Brayton cycle system and thermodynamic analysis[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2022, 43(2): 32-39(in Chinese).
[9] WRIGHT S A. Preliminary results of a dynamic systems model for a closed-loop brayton cycle system coupled to a nuclear reactor[C]//Proceedings of the 1st International Energy Conversion Engineering Conference (IECEC). Virigina: AIAA, 2003.
[10] WRIGHT S A, TRAVIS S. Dynamic modeling and control of nuclear reactors coupled to closed-loop Brayton cycle systems using SIMULINK[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2005, 746(1): 991-1004.
[11] TAUVERON N, SAEZ M, MARCHAND M, et al. Transient thermal-hydraulic simulations of direct cycle gas cooled reactors[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2005, 235(23): 2527-2545. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2005.05.033
[12] MAUGER G, TAUVERON N, BENTIVOGLIO F, et al. On the dynamic modeling of Brayton cycle power conversion systems with the CATHARE-3 code[J]. Energy, 2019, 168: 1002-1016. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.11.063
[13] MCCANN L D. Use of RELAP5-3D for dynamic analysis of a closed-loop brayton cycle coupled to a nuclear reactor[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2007, 880(1): 541-550.
[14] LIU Z, CHENG X, YANG X, et al. Ultra-high temperature microstructural changes of SiC layers in TRISO particles[J]. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(1): 2331-2339. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.11.007
[15] 朱继洲, 奚树人, 单建强, 等. 核反应堆安全分析[M]. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 2000.



 下载:
下载: